This web page was produced as an assignment for Genetics 677, an undergraduate course at UW-Madison
Phylogenetic Analysis
Phylogenetic trees are useful tools when determining evolutionary relatedness amongst different organisms. They allow us to easily observe homology between different species. After determining genetic homology between different organisms, one puts that information into a phylogenetic tree to see how closely related the organisms are according to the information you are looking at. In this case, I used the homology data of the hcrtr1 gene that I obtained from the HomoloGene website:
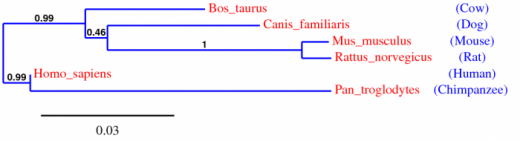
Figure 1: The tree above was generated using Phylogeny.fr (Robust Phylogenetic Analysis for the Non-Specialist). It was created using "A La Carte" Mode with the processing steps: "Multiple alignment: T-Coffee, Alignment curation: Gblocks, Construction of phylogenetic tree: Maximum likelihood, Visualization: TreeDyn".
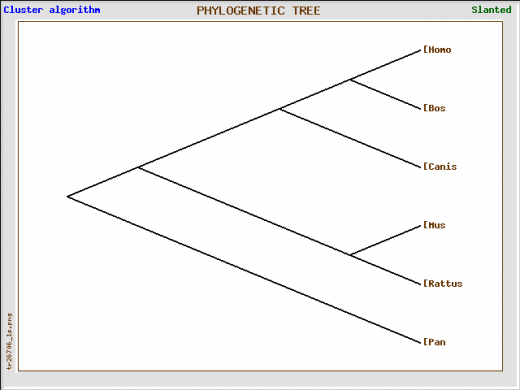
Figure 2: The tree above is a different depiction of Figure 1. The same information was used.
Analysis
The trees show a high degree of homology in the hypocretin receptor 1 protein. It is interesting to note that chimpanzees show the highest similarity in the hcrtr1 gene which makes sense because chimpanzees are the closest relative to humans. The next closest linked homologs are cattle and after that dogs. Dogs are another organism known to be affected by narcolepsy. All of the information from the phylogeny website agrees with the homology information determined from the HomoloGene website.
References:
(1) Figure 1, 2: Phylogeny.fr. Marseille, France: Marseille-Nice Genopole; June 2009. Available from: http://www.phylogeny.fr/version2_cgi/index.cgi
Eric Suchy, Email: [email protected], last updated: May 15, 2010