This web page was produced as an assignment for Genetics 677, an undergraduate course at UW-Madison
General Protein Data
Name: Orexin receptor type 1 (Hypocretin receptor type 1)
Accession number: O43613
Sequence Length: 425 Amino Acids long
Function: selective excitatory receptor for orexin-A and orexin-B neuropeptides
Sequence Similarities: Belongs to G-protein coupled receptor 1 family
Accession number: O43613
Sequence Length: 425 Amino Acids long
Function: selective excitatory receptor for orexin-A and orexin-B neuropeptides
Sequence Similarities: Belongs to G-protein coupled receptor 1 family
G-protein coupled receptors
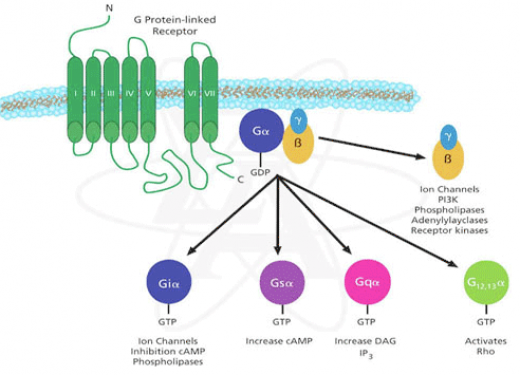
The hypocretin receptor protein belongs to a large family of proteins called the G-protein coupled receptors. These receptors are transmembrane proteins which sense ligands outside of the cell and bind them. In the case of hypocretin receptor 1, the ligand that is bound to the receptor is a neuropeptide called hypocretin 1. The binding of the extracellular ligands forces a conformational change in the receptor and allows it to activate an associated G-protein by exchanging a bound GDP for a GTP. The activation of the G-protein results in affecting signal transduction pathways and other intracellular signaling. This is how an extracellular molecule can influence internal cellular processes.
Figure 1: The figure above depicts the process of G-protein coupled receptor protein cell signaling. It also depicts the diversity of the signaling. Depending on the type of subunit isoform, different signals can be induced.
References:
(1) Uniprot website
(2) Gilman A.G. (1987). "G Proteins: Transducers of Receptor-Generated Signals". Annual Review of Biochemistry 56: 615–649. doi:10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. PMID 3113327.
(3) Figure 1. Schoneberg, T., et al., Structural basis of G protein-coupled receptor function. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol., 151, 181-193 (1999).
(2) Gilman A.G. (1987). "G Proteins: Transducers of Receptor-Generated Signals". Annual Review of Biochemistry 56: 615–649. doi:10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. PMID 3113327.
(3) Figure 1. Schoneberg, T., et al., Structural basis of G protein-coupled receptor function. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol., 151, 181-193 (1999).
Eric Suchy, Email: [email protected], last updated: May 15, 2010